The electronic structures of topological materials have a property which is invariant under some topological continuous deformation. Topological materials consists of various types such as topological insulators, topological semimetals, topological superconductors and so on.
Topological insulators are materials with conducting surface states and insulating bulk states. Backscattering of the surface states by nonmagnetic impurities is prohibited, which may lead to wide applications in spin engineering. The most definite evidence of topological insulators is the existence of spin-polarized Dirac-bands at the surfaces. In contrast, topological semimetals, such as Dirac semimetals, Weyl semimetals, topological nodal-line semimetals, host Dirac bands in the bulk. Topological semimetals have some interesting properties, such as Fermi arc states, monopoles of Berry curvature in momentum space, resulting in unique electric transports.
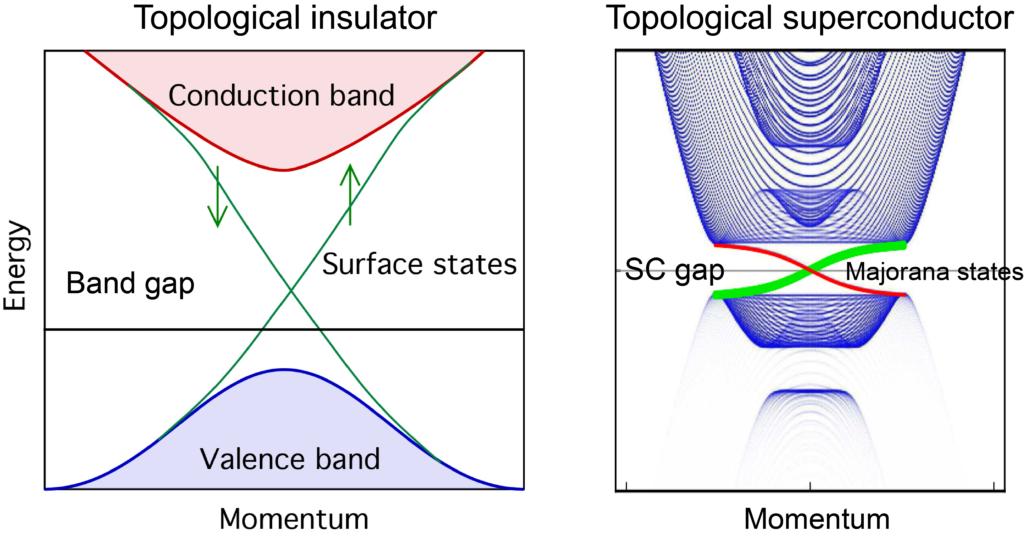
When the electronic structure of superconducting Bogoliubov quasiparticles is topological, the material is a topological superconductor. There are Majorana states at the surface/edge of a topological superconductor, which satisfy non-abelian statistics. It is proposed that the proximity effect between a topological insulator and an s-wave superconductor can produce topological superconductivity at the interface. This proposal can be realized in a heterostructure of a topological insulator and an s-wave superconductor. In iron-based superconductors, the topological insulator state and the superconducting state coexist in a single crystal, which is much easier to fabricate and study than a heterostructure. Iron-based superconductors provide a simple and high-Tc platform to study topological superconductors.

